You can access the distribution details by navigating to My Print Books(POD) > Distribution
Description
Space-Time
ABSTRACT
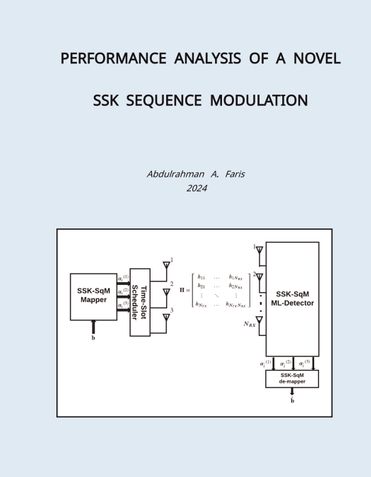
This thesis is concerned with developing a novel way of transmitting information using non- modulated symbols in sequence. In this scheme, which is named Space Shift Keying-Sequence Modulation (SSK-SqM), multiple time-slots are used. This enables the proposed scheme to accommodate the use of an odd number of transmit antennas instead of a multiple power of two in the cutting-edge technology of spatial modulation schemes.
The proposed technique in this thesis is based on a unique sequence of frequency-flat fading channels, on an incoming pattern of information bits. The flat-fading channels transmit data exclusively in the spatial domain. The proposed mapping table for the transmitter is utilized to build a system model equation. The suggested technique additionally incorporates the derived system model equation and a simple maximum likelihood detector. In a single-input-multiple- output (SIMO) setup, a validation framework is established by utilizing the mutual information (MI) and sample variance (SV) criteria. The closed-form theoretical performance framework for noise and flat-fading was then validated with a Monte-Carlo simulation, which was tightly bounded. Simulations were carried out on Octave Software with the use of a signal processing package.
The proposed scheme results show that a sequence of channels can be used as transmit entities in index modulation. At the same time, enjoy the benefits of classical spatial modulation with enhanced information security. The performance of the proposed model was evaluated using bit error performance curves under the Additive White Gaussian Noise (AWGN) channel model in flat-fading channels. Performance curves for the simulated transmission were compared with theoretical bit error rate (BER) curves. The Rayleigh channel was shown to perform better than the Rician when performance curves were compared. This was due to the fact that high scattering of Rayleigh paths contributed to a low probability of error as the paths are used for conveying information. The use of unique pattern assignment in the mapping table also provides some security since the information can only be decoded if the same table is known at the receiver. This was shown by a secrecy rate analysis employing a wiretap model. The proposed model outperformed both the SIMO (Single-Input-Multiple-Output) and classical SSK in terms of secrecy rate. The secrecy enhancement in the SSK-SqM, suits it well in security sensitive scenario / systems such as in military, vehicle-to-vehivle (V2V) communication, as well as space communication system. A reduction of about fifty percent in receiver computational
complexity was achieved in comparison to other state of the art techniques. The proposed model can be generalized to accommodate various sets of receiver antennas in future work, also using generalized fading distribution such as Nakagami-m as transmit entity.
Book Details
Ratings & Reviews

Currently there are no reviews available for this book.
Be the first one to write a review for the book Performance Analysis of a Novel SSK Sequence Modulation.
Other Books in Engineering, Science & Technology
Rohit Chaurasia
ER. ARIF KHAN
Dr. Manoj C. Kandpal, Dr. Ashok Kumar, Prof. ...
EFY Enterprises Pvt Ltd